Gout Signs and Treatments You Should Know
- Jusrandomly

- Jul 23
- 3 min read
Gout is an inflammatory form of arthritis brought on by the buildup of crystals of uric acid within the joints. It may suddenly attack, usually at night, and produce severe pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness in the area of the attacked joint—usually the big toe. Although gout has traditionally been linked to monarchs because of its connection to rich food and wine, it's a widespread disease that strikes millions of individuals on earth today.

What Causes Gout?
Gout occurs when your body makes too much uric acid or when your kidneys are unable to flush out enough. Uric acid is a byproduct of purines—natural chemicals in some foods and body tissues.
If uric acid accumulates in the blood, it can crystallize and deposit in joints, resulting in inflammation and excruciating pain. This is known as hyperuricemia.
Common Risk Factors:

A diet rich in red meat, shellfish, and sugary drinks
Alcohol use (particularly beer)
Obesity
Certain medications (such as diuretics or aspirin)
Genetics
Chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease
Early Symptoms of Gout
Gout does not necessarily scream its presence initially. You may experience slight discomfort that goes away, then comes back later in the form of an actual attack. Identification of these early symptoms allows you to timely seek treatment and minimize complications.

1. Acute Joint Pain
Usually occurring at night, pain usually starts in the large toe (termed podagra), but other joints in the ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers may be affected.
2. Swelling and Redness
The inflamed joint swells, reddens, warms, and becomes very sensitive to touch, sometimes even causing difficulty in wearing shoes or walking.
3. Lingering Discomfort
Once the worst pain has passed, there can be lingering joint pain for several days or weeks—particularly with frequent recurrences.
4. Limited Range of Motion
Joint stiffness and decreased mobility may occur in chronic gout, especially when uric acid levels are uncontrolled.
5. Tophi (Chronic Gout Bumps)
In time, uric acid crystal deposits known as tophi may develop beneath the skin. These may show up on fingers, elbows, ears, and joints, indicating long-standing, untreated gout.
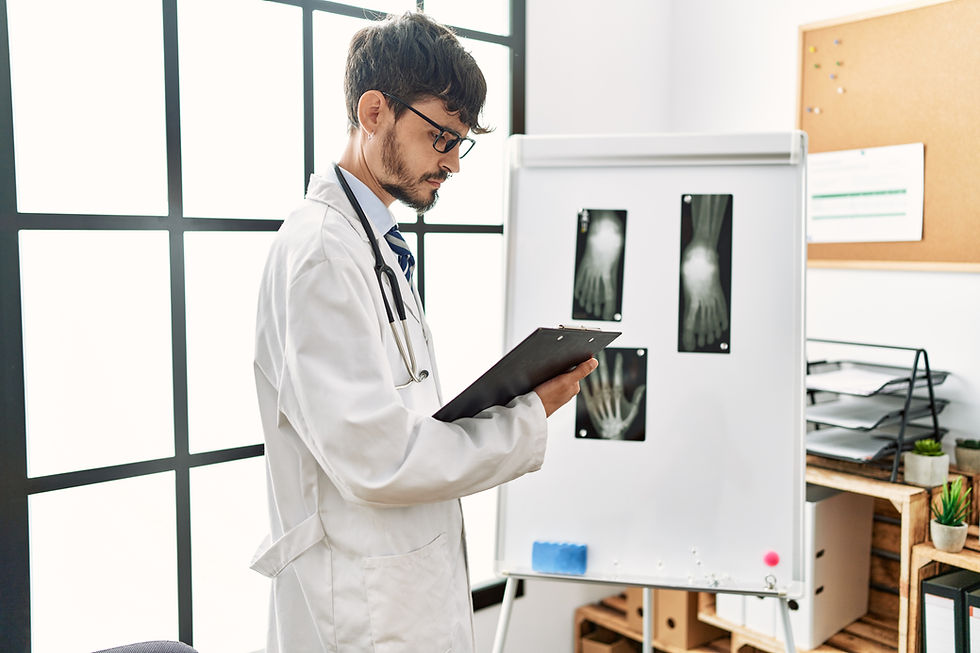
How is Gout Diagnosed?
Your physician will take into account:
Medical history and signs
Blood tests to assess uric acid level
Joint fluid analysis (joint fluid aspiration)
X-rays or ultrasound to identify tophi or joint injury
Treatment for Gout
Successful treatment of gout requires short-term relief during attacks and long-term control to avoid future flares and complications.
1. Acute Gout Medications

These medications relieve pain and inflammation rapidly:
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs)
Colchicine
Corticosteroids
2. Long-term Uric Acid Control
To avoid future gout attacks, physicians prescribe medications that reduce uric acid production or assist in removing it from the body.
3. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
A key part of managing gout is making long-term lifestyle adjustments.

Diet Tips for Gout:
Avoid purine-rich foods: red meat, liver, anchovies, sardines, and shellfish
Reduce sugary drinks, especially those containing high fructose corn syrup
Limit alcohol—beer and spirits are major gout triggers
Eat low-fat dairy products, cherries, and vitamin C-rich foods (they may help lower uric acid)
Stay hydrated—drink plenty of water
Other Lifestyle Modifications:
Lose weight if overweight
Excess body fat increases uric acid production and reduces kidney efficiency.
Exercise regularly
Choose low-impact exercises to protect your joints.
Manage stress
Chronic stress can induce inflammation or exacerbate attacks.
Can Gout Be Cured?
There is no lifelong cure for gout, but it can be managed quite well with timely diagnosis, proper treatment, and regular lifestyle modifications. Most gout sufferers lead healthy, pain-free lives when they adhere to a treatment regimen and adhere to dietary guidelines.
What are the Complications of Untreated Gout?
Untreated gout may cause:
Chronic arthritis and joint damage
Kidney stones (due to uric acid deposition in kidneys)
Formation of tophi, leading to joint deformity
Decreased quality of life due to recurrent and severe pain
When to see a Doctor?
Consult a doctor immediately if you:
Feel sudden, severe joint pain
Have red, hot, or inflamed joints
Notice bumps or nodules beneath the skin
Need to initiate medications for prevention
Early treatment avoids permanent joint damage and significantly improves outcomes. Disclaimer:
The content provided on Jusrandomly is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Jusrandomly does not promote or advise the use of any specific treatments, medications, supplements, or practices discussed in this article. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health routine or taking any medication. Relying on the information provided on this site is solely at your own risk.








Comments